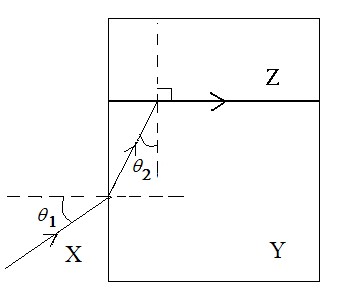
In the diagram shown below, a ray of monochromatic light travels from a material X with refractive index
n1 = 1.63 to a material Y with refractive index
n2 = 1.57 and grazes the interface with a material Z of an unknown index of refraction
n3 at 90 º. If the angle of incidence of the ray is
θ1 = 32.1º, what is the unknown index of refraction
n3 of the material Z?